Chapter 6 Loop Statement
6.2 For Loop¶
The for statement is a second looping statement. It can be used to iterate through a container object. The syntax of the for statement is shown in Fig. 6.3, which begins with a line that consists of the for keyword, followed by an identifier, and then the in keyword, and then a container object, and finally a colon.
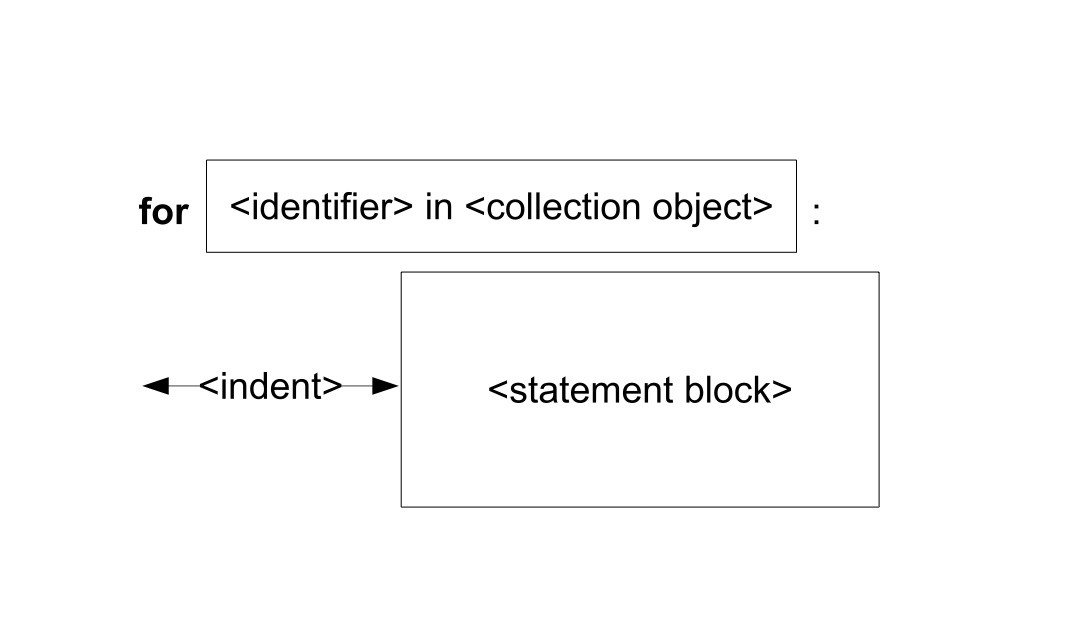
Fig. 6.3 The for statement¶
After the for line is an indented statement block, which is executed repeatedly, once for each element in the collection object. In each iteration, the current element of the collection is assigned to the identifier after the for keyword, which serves as the loop variable. For example, the following code iterates through a collection generaged by range function, printing out each element from 0 to 9:
In the example above, the for statement consists of two lines, the first being the for line with the loop variable being defined as x, and the second line being an indented statement block that consists of a single statement. When executed, the for statement iterates through all elements of the collection, assigning the current element to the identifier x at each iteration, before executing the indented statement block, or loop body. As a result, the dynamic execution sequence of the example above is:
x=0
print (x)
x=1
print (x)
x=2
print (x)
.....
x=9
print (x)
An equivalent loop using the while statement is:
In the example above, the variable i is used as the loop variable. It iterates through the values 0, 1, … , len(t). At each iteration, a corresponding element t[i] is taken from the container t, and assigned to the variable x. This type of iteration through a container object is called traversal. Compared with the while loop, the for loop is more convenient for performing collection traversal. Since using a for statement, the additional loop variable i is unnecessary. Container objects that can be iterated through using a for loop are also called iterable objects.
Check your understanding
- a for-loop or a while-loop
- Although you do not know how many iterations you loop will run before the program starts running, once you have chosen your random integer, Python knows exactly how many iterations the loop will run, so either a for-loop or a while-loop will work.
- only a for-loop
- As you learned in section 7.2, a while-loop can always be used for anything a for-loop can be used for.
- only a while-loop
- Although you do not know how many iterations you loop will run before the program starts running, once you have chosen your random integer, Python knows exactly how many iterations the loop will run, so this is an example of definite iteration.
6.2Q-1: Which type of loop can be used to perform the following iteration: You choose a positive integer at random and then print the numbers from 1 up to and including the selected integer.
- 10
- Iteration by item will process once for each item in the sequence.
- 11
- The blank is part of the sequence.
- 12
- Yes, there are 12 characters, including the blank.
- Error, the for statement needs to use the range function.
- The for statement can iterate over a sequence item by item.
6.2Q-2: How many times is the word HELLO printed by the following statements?
s = "python rocks"
for ch in s:
print("HELLO")
- 4
- Slice returns a sequence that can be iterated over.
- 5
- Yes, The blank is part of the sequence returned by slice
- 6
- Check the result of s[3:8]. It does not include the item at index 8.
- Error, the for statement cannot use slice.
- Slice returns a sequence.
6.2Q-3: How many times is the word HELLO printed by the following statements?
s = "python rocks"
for ch in s[3:8]:
print("HELLO")
- 0
- The for loop visits each index but the selection only prints some of them.
- 1
- o is at positions 4 and 8
- 6
- Yes, it will print all the characters in even index positions and the o character appears in an even location.
- Error, the for statement cannot have an if inside.
- The for statement can have any statements inside, including if as well as for.
6.2Q-4: How many times is the letter o printed by the following statements?
s = "python rocks"
for idx in range(len(s)):
if idx % 2 == 0:
print('o')
- Ball
- Each item is converted to upper case before concatenation.
- BALL
- Each character is converted to upper case but the order is wrong.
- LLAB
- Yes, the order is reversed due to the order of the concatenation.
6.2Q-5: What is printed by the following statements:
s = "ball"
r = ""
for item in s:
r = item.upper() + r
print(r)
Note
This workspace is provided for your convenience. You can use this activecode window to try out anything you like.
© Copyright 2024 GS Ng.